Mosaic cameras are specifically designed to integrate seamlessly with your preferred external sensors.
The Growing Demand for Integrated Systems
Every project and workflow is different, and your equipment options should reflect that! Mosaic mobile mapping systems stand out from the crowd with endless integration options thanks to engineering that keeps customers at the forefront.
As urban environments become increasingly complex and data volumes continue to grow, professionals require tools that work together reliably, particularly when capturing both visual and geospatial data. In mobile mapping systems, this often means combining external sensors, such as LiDAR, GNSS, and INS/IMU, with high-resolution 360° imagery.
Mosaic’s camera systems are engineered from the start with this need in mind. Unlike many imagery solutions, they do not force users into closed software ecosystems or rigid workflows. Instead, Mosaic offers open, flexible hardware that integrates cleanly with LiDAR, GNSS, and other sensors. This flexibility has positioned Mosaic cameras as a reliable 360° imaging core in many multi-sensor systems.

Why visual and geospatial data must work together
LiDAR excels at producing dense, accurate 3D point clouds, GNSS positions the imagery within space, and INS/IMU tells us the speed of travel. However, without accompanying imagery, these datapoints often lack visual context.
To achieve meaningful results for projects that require asset inspections, road condition monitoring, or digital twin creation, professionals need multiple data types that are aligned accurately and captured synchronously.
Visual context is important for communicating project details to those outside the professional scope of the project. Clients, investors, and taxpayers are just a few examples of individuals who benefit from visual accessibility beyond highly technical point clouds and charts. Having visuals alongside geospatial data adds credibility to projects for those who lack the technical expertise to decipher data from external sensors.
Integrating cameras with external sensors has historically been a difficult challenge. Many camera systems lack accurate timestamping, precise triggering, or robust ports to handle GNSS/INS connections. Mosaic addresses all of these pain points with design choices that specifically prioritize open access, synchronization, and hardware-level integration.

5 reasons why Mosaic cameras integrate seamlessly
We’ve engineered Mosaic’s mobile mapping systems at every step to integrate seamlessly with a variety of devices across the geospatial industry.
1. Open architecture and no vendor lock-in
Many camera systems impose rigid restrictions. They either require users to license proprietary software or prevent access to source data. At Mosaic, we empower our users, not restrict them. Our cameras are built on a philosophy of openness, providing integrators with complete freedom to design their ideal mobile mapping system. We offer an open architecture that prioritizes user control and long-term flexibility.
Full API access
Mosaic provides a REST API (Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface) that gives complete programmatic control over the camera. This includes starting and stopping capture, adjusting image settings, and/or initiating diagnostics. Integration engineers can automate capture workflows or sync image acquisition with external sensors using software triggers.
Accessible source data
We don’t lock you into a proprietary ecosystem! You have direct access to core files: h.264 video streams, frame-level timestamps, and GNSS logs. These are stored on SSDs using standard file systems, making post-processing simple and transparent. Extract individual frames, align imagery to point clouds, and feed them into your preferred SLAM, GIS, or photogrammetry pipeline. No proprietary viewers required!
No forced subscriptions
With Mosaic cameras, there are no subscription models or forced processing platforms. Mosaic provides the hardware, and you decide how and where to process the data. This is especially valuable for teams already using in-house pipelines or third-party point cloud software.
Your data stays safe and accessible on servers of your choosing. No more worrying about software subscriptions running out, a missed payment, or security concerns regarding cloud-based data. Avoid violations of GDPR, CCPA, and other data security regulations that apply to storing data with third-party services.
However, if you are in the market for new software, check out Mosaic’s suite of post-processing tools, which include the following:
- Mosaic Processor, to stitch & georeference imagery,
- Mosaic Anonymizer, which protects the privacy of image subjects with anonymization of faces and license plates, and the
- Mosaic 3D Tool to simplify complex 3D reconstructions.
2. Precision synchronization with LiDAR and GNSS/INS
The single most critical factor in a multi-sensor system is timing. If images do not precisely sync with geospatial data, it results in mismatched maps, blurry textures, and/or incorrect geolocation.
Our cameras are designed to act as the precise “heartbeat” of a mobile mapping system, ensuring every photo aligns exactly with data from external sensors, such as LiDAR and GNSS/INS.
Support for external timestamps
While Mosaic cameras include internal GNSS modules, they also support synchronization from external GNSS/INS sources. This provides higher accuracy and consistency, which is crucial for high-speed capture or operating in GNSS-denied areas, such as urban canyons or tunnels. It also gives your team the flexibility to work with the external GNSS/INS technology they’re most comfortable using.
PPS and NMEA inputs
Through its AUX port, the camera accepts both a Pulse-Per-Second (PPS) signal and standard NMEA messages. The PPS signal ensures nanosecond-level timing accuracy, and the NMEA data provides precise GNSS location, heading, and system status. Together, these inputs enable the camera to operate as a time-locked imaging device within a larger system.

3. Flexible triggering options for real-world conditions
Data collection shouldn’t be one-size-fits-all. There are multiple ways to trigger Mosaic cameras, allowing for dynamic and efficient data capture that can be controlled by other sensors or real-world conditions.
In dynamic field environments, rigid capture intervals often cause poor or incomplete datasets. With Mosaic cameras, integrators have multiple trigger options, allowing them to react to distance, time, or external pulses.
Distance-based triggering
Using a reliable GNSS signal, the camera can capture imagery at predefined intervals, for example, every five meters. This is ideal for corridor mapping, road inspections, or other linear infrastructure surveys. It is also ideal for cityscapes, as waiting at red lights and crosswalks makes images captured with time-based triggering redundant.
Time-based triggering
In its default configuration, the camera operates in free-running mode. It captures images at a set frame rate, indicated as FPS (frames per second). This is useful when mapping areas without strong GNSS or when regular time-based intervals are acceptable, such as driving down a highway at a set speed.
Triggered by an external pulse
The AUX port’s opto-isolated GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) enables external sensors, such as LiDAR, wheel odometers, or IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units), to trigger the camera. This allows engineers to tie image capture directly to other system events.
For example, the LiDAR can emit a pulse every time it captures a new sweep, and that same pulse can be used to trigger the camera. This creates an accurate 1:1 match between the point cloud and a 360° image.
4. Robust, industrial-grade connectivity
A successful integration requires reliable physical and electrical connections that can withstand real-world field conditions. We use industrial-grade, standard interfaces for maximum reliability and compatibility.
Centralized AUX connector
This single, robust port handles a variety of integration signals: power, RS-232 for data communication (NMEA), PPS input, GPIO input (triggering), and GPIO output (end-of-exposure). This compact design simplifies wiring and reduces potential failure points.
Ethernet connectivity
Each Mosaic camera includes a 1 GbE Ethernet port. This supports stable control, live preview, and system monitoring. It also allows remote operation of the camera from inside a vehicle or a mobile command station.
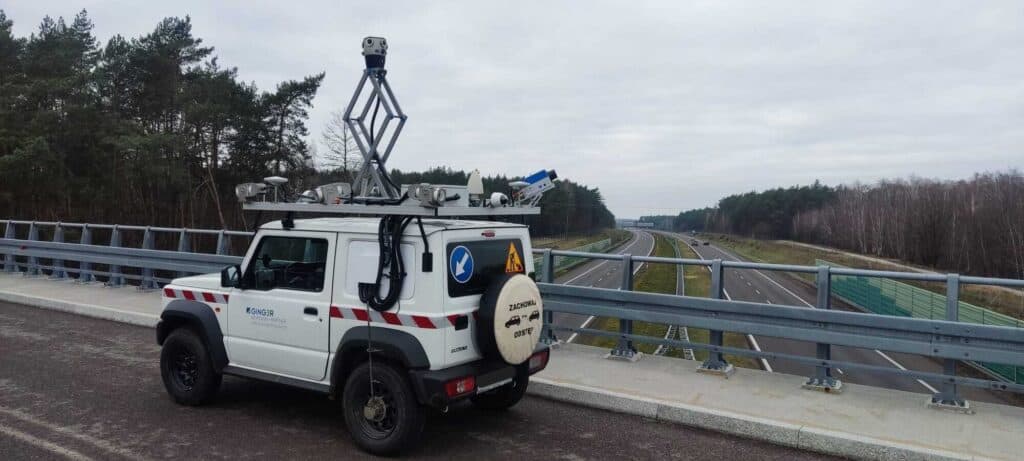
Purpose-built mounting
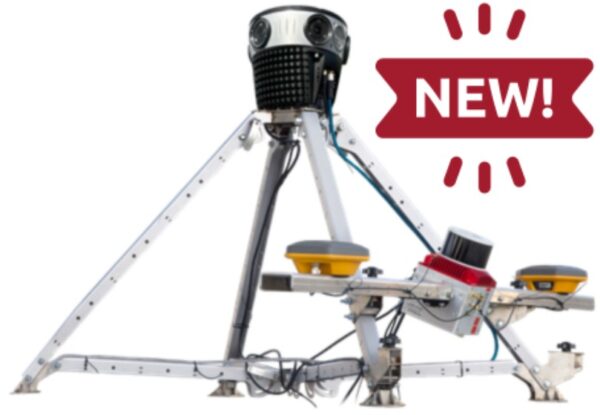
Mosaic mounting solutions, such as the Mosaic Travel Mount, are designed with sensor integration in mind. They feature ample physical space and attachment points for external GNSS antennas, IMUs, and other devices. This reduces custom fabrication work and ensures all components maintain fixed orientation during capture.

5. A field-proven ecosystem with industry validation
Our cameras have already proven themselves in the field, featuring a wide range of industry-leading sensors. This demonstrates their capability and provides integrators with a clear path to success using tested and verified components.
High-End INS compatibility
We offer seamless, out-of-the-box integration with top-tier Inertial Navigation Systems, such as the Movella (Xsens) Vision Navigator, enabling centimeter-level accuracy even in GNSS-denied environments.
Reliable GNSS options
We support and have tested integrations with widely used RTK GNSS receivers, such as the Emlid Reach RS2.
LiDAR compatibility
The combination of precise triggering and synchronization makes our cameras the ideal imaging component for high-end LiDAR scanners, such as those from RIEGL, as demonstrated by our all-in-one Mosaic Meridian system. It combines 360° imaging with LiDAR and GNSS/INS into a compact unit. It is already being used in professional mapping projects worldwide.

Is your external sensor system our next integration?
Why should you rearrange your workflow around your equipment? Surveying equipment should be working for you! Reach out today to learn more about Mosaic’s flexible integration options.