How to create the most realistic virtual sets using a 360 camera array
Virtual Sets & Virtual Studios – Revolutionizing Film Production
If you’ve seen The Mandalorian and you’ve wondered why it looked SO REAL, then you have come to the right spot. Learn how the Mandalorian utilized a breakout technology – an in-camera virtual set – to bring the most life-like experience to viewers around the globe.
The Evolution of Filming and the Use of Screens
To fully appreciate how far we’ve come since the invention of film and the film industry (just over a century old), let’s have a look at the evolution of film, in particular, how directors created backgrounds when they were not able to film the scene live.
Single screen behind an actor
- Remember those horribly fake-looking backgrounds in EVERY driving scene in movies? The actors always moved the steering wheel in such a jerky fashion, while the background stayed in the same viewpoint. Who drives like that anyway?!
- Problems with a single screen: If the director wanted to move the camera angle during the scene, the projected footage couldn’t move with the camera. Directors had to work with a single camera angle when filming a chase scene.
Green screens or Chroma Keying
- Actors act in front of a literal green screen. Due to the way green reacts on film, you can film a blank background and later digitally remove or “key out” that color. Now, you can drop the scene onto the background of your choice in post-production.
- Problem with Green Screens: actors have to imagine their environment. Just think about how difficult it must have been to film a whole fight scene from the Avengers movies in which the alien invaders were falling from the sky. The actors had to visualize all of that mentally and react accordingly. I know action films often get a lot of heat for the less-than-stellar acting, but perhaps they’re better than we think if they can make us believe they are fighting armies of invaders when, in fact, they are surrounded by bright neon walls.
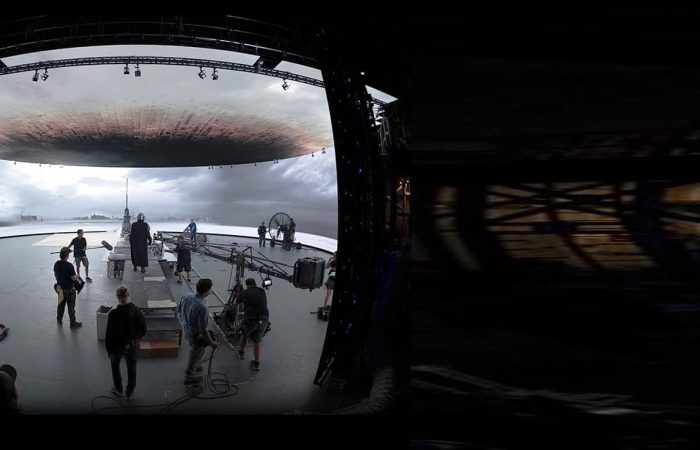
LED screens/wall technology
- Digitally created or real-life footage is displayed on a large collection of LED screens, usually in a semi-circle formation, creating a wall and ceiling
- Benefits of LED screens: actors can see their environment on the screens at the appropriate time and react accordingly
No, you’re not imagining things – it is a virtual set. The walls and ceiling are dozens upon dozens of LED screens fitted together and displaying an incredibly clear, true-to-life environment. Now, the actors can ‘play’ in front of it.
With the touch of a few buttons, the director can change that gorgeous twilight sky into a fiercely bright midday blaze.
What is the difference between a set and a virtual set (or virtual studio)?
A virtual set is a collection of several extremely novel technologies which project a life-like environment onto LED screens located behind actors while filming a scene for a movie or TV show. These are the two biggest uses now, but theoretically, any sort of film production will benefit from this technology in the near future.
A virtual studio allows for real objects and real people (actors) to seamlessly interact in real-time with computer-generated environments and objects.
What is virtual production?
The key element of a virtual set is that the real-life camera on set can move in 3D space, while the image from the virtual camera renders from the same perspective. The different camera settings – pan, angle, zoom, traveling – can adapt at any time to be in tune with the actors.
Unlike older technologies, virtual production happens in real-time and does not require post-production work.
How Virtual Sets Will Dominate the Previous Filming Solution
Virtual sets are already becoming the norm in many high-end film productions due to the many benefits and very few drawbacks.
The benefits of using a virtual set
Motion-tracking creates hyper-realistic scenes
Using Unreal Engine (a 3D video game “engine”), artists can create a photorealistic 3D background that moves strictly with the camera’s field of view (aka: frustum), so if the camera swings around and changes angles, the background shifts in precisely the same way. This allows motion-tracked cameras to execute traditional cinematography techniques within the virtual set, achieving cinematic movements like the parallax effect (object in the foreground moves at a different speed than the background). This amplifies the illusion of filming at an actual location.
Solves the problem of lighting
Light coming from LEDs provides realistic colors and reflections on the actors and props (not possible with green screen)
Removes green spill
This refers to the green light that reflects onto the actors and props from the green screens. Everything gets a greenish glow.
Big impact on time and budgets
Because we confine most virtual sets to a particular area, they need less space overall.
Developing and building the LED screens is definitely expensive the first time, but the initial investment will soon pay off. It saves on traveling to locations, building new sets, and the costly post-production
Customization of the features
Artists and directors can make changes and control the world on the day of shooting
Exposure, color, animation playback, and fill lighting are available
Can move a mountain with the press of a finger
Still able to use green screens within an LED wall
It is still possible to use a specific portion of the LED and transform it into a green screen.
Ex: Can remove people and add additional action behind them
This is because some special effects are still best done traditionally, which prevents damaging the LED screens.
Speed of setup
Rather than traveling to different locations or setting up in-studio sets, setting up a virtual set is faster. Also, when working within a normal set, changing the lighting can add significant time to each shot as cranes and lights have to be moved around and adjusted often.
How to create virtual sets
Let’s look at the technologies, as well as the steps and the people needed to create a virtual set.
Technologies necessary for creating a virtual set
There exist many technical solutions for creating virtual sets and studios, but most of them include the following components:
Optical or mechanical measurements create a live stream of data describing the exact perspective of the camera in camera tracking.
Real-time rendering software uses the camera tracking data and generates a synthetic image of a television studio.
A video mixer combines the video from the camera with the video from the real-time rendering software to produce a final video output. Replacing a chroma key background is one of the most common ways to mix the video.
Steps to creating and using virtual sets
While the actual steps involved are much more complicated than what can be covered here, we will focus on why this affects Mosaic. For a more thorough understanding of the ins and outs of creating a virtual set, check out this incredible article here.
We will stick to what we know – data capture. That’s why we’re so excited for our Mosaic cameras and mobile mapping services, particularly for innovative technologies like in-camera VFX on virtual sets.
Hopefully, at this point, we all understand that a virtual set is basically the way in which actors can film in front of a flat backdrop but feel as if they are in an actual, real scene. The imagery on those LED screens has to come from somewhere, though, right?
Who is behind creating virtual sets?
There are several methods for displaying images on virtual set LED screens.
- Option A: 3D graphic artists and 3D computer graphics software
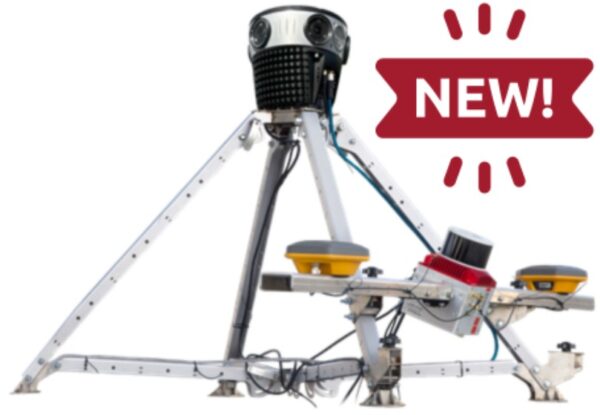
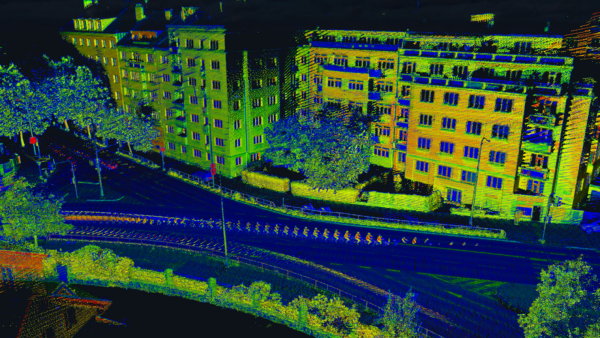
- Option B: capture real-life images (and generate complete 3D models of large-scale scenes) with the highest resolution camera array on the market today.
This is where we get involved and why we’re so amped up! The images portrayed on these screens have, for now, been created through the hard work of 3D graphic artists and 3D computer graphics software, who create virtual backgrounds and all of the bells and whistles that go along with making a scene look real.
The Mandalorian, in particular, used images and environments sourced from Unreal Engine. This library for super advanced, super real-time 3D creations is very helpful. Up until now, this technology was in the gaming industry for those almost-too-realistic first-person shooter games.
But Mosaic cameras, with the highest resolution camera array in the world, collect 3D environments faster and more efficiently than 3D graphic artists.
With image capture abilities from a camera array that is expertly synchronized to collect a full 360-degree view of the surrounding area, film production has a brand new tool at its disposal. They can effortlessly gather real-life data in almost no time at all, thereby reducing time and resources significantly.
Check out some of these videos captured by the Mosaic Viking – the world’s highest resolution camera.
The future of film production
Certainly, 3D artists, VFX specialists, and complementary software will be necessary when creating the content for fantasy films or shows. For those situations, the virtual environments will need to be carefully crafted for directors’, producers’, and writers’ needs.
However, for scenes which are set in real-life places – downtown Hong Kong, the middle of Santiago Bernabéu Stadium (Real Madrid), or the depths of the Amazon forest – there will be a much faster, easier, and cost-efficient manner in which the image data is collected.
If you are interested in more information about the Mosaic line of cameras or our data collection services, feel free to drop us a line below.